Table of Contents
Being a parent entails looking out for your child attentively observing every sound they produce including their breath. When your child begins to pant, particularly during periods of excitement, it may be a joyful and confusing experience. Babies that pant, which is characterized by shallow, fast breathing, frequently have worries about whether this is normal and what it means for their health. This activity, similar to the eager breaths of a playful puppy, not only produces a bodily response but also provides crucial knowledge about your baby’s emotional and developmental circumstances.
I’ve learned to negotiate these times of excitement and uncertainty throughout my journey as a parent. While it is frequently a normal aspect of a baby’s growth, panting can also indicate a need for medical care or testing. The secret is to comprehend the subtleties of this conduct. In response to the urgent query, “Is baby panting when excited a cause for concern?”, most of the time it is a normal, healthy manifestation of their developing emotional and physical maturation. To protect your baby’s health and happiness, however, you must be aware of the situation and on the lookout for any associated symptoms.
Understanding Baby Panting
One amazing feature of newborn development is the panting of the child. You may notice that your infant breathes quickly and shallowly when they are enthusiastic or engaged. However, what precisely is going on at these times? Let us dissect it into four main points:
1. Physical Response to Excitement: Babies’ respiratory systems quicken their breathing in response to excitement. This is the body’s response to the elevated mood and heightened level of exercise.
2. Expression of Emotion: Babies have few methods to communicate, yet they can indicate delight, excitement, or anticipation by panting at a person, object, or activity.
3. Developmental Milestone: Babies get better at controlling their breathing as they get older. Panting may indicate that they are investigating and gaining control of their breathing.
4. Indicator of Health: Although frequently typical, the pattern and frequency of your baby’s panting might also reveal how well their respiratory system works.
You Might Also Like to Read: Can I Mix Baby Oatmeal with Water?
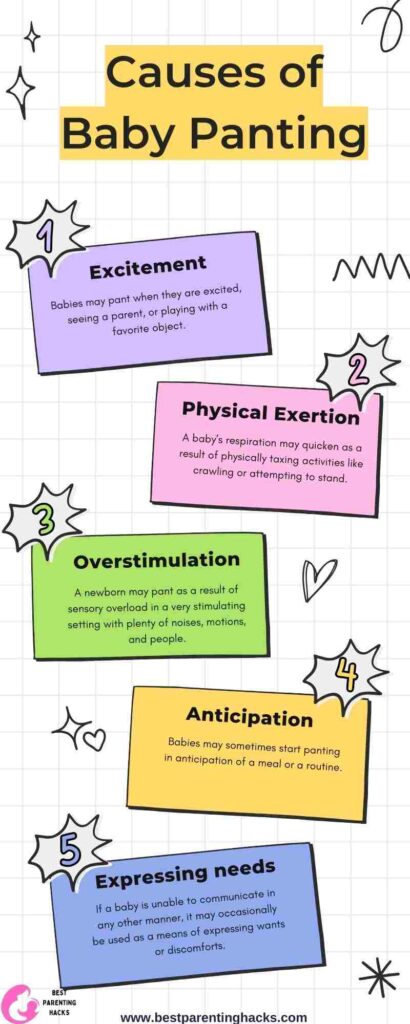
Causes of Baby Panting
Numerous reasons might be responsible for a baby’s panting:
1. Excitement: Babies may pant when they are excited, seeing a parent, or playing with a favorite object.
2. Physical Exertion: A baby’s respiration may quicken as a result of physically taxing activities like crawling or attempting to stand.
3. Overstimulation: A newborn may pant as a result of sensory overload in a very stimulating setting with plenty of noises, motions, and people.
4. Anticipation: Babies may sometimes start panting in anticipation of a meal or a routine.
5. Expressing needs: If a baby is unable to communicate in any other manner, it may occasionally be used as a means of expressing wants or discomforts.
You Might Also Like to Read: Baby’s Breath Smells Like Yogurt. What’s the Reason?

When Do Babies Begin Panting?
Several criteria must be taken into consideration to determine when newborns normally start panting:
1. Age: As they become older, babies may begin to pant as early as a few months, however, the frequency and severity of their panting will change.
2. Physical Development: Babies experience various breathing habits, such as panting, as their lungs and respiratory systems grow.
3. Emotional Development: Babies may start panting in reaction to excitement as they learn to express themselves and react to their surroundings.
4. Activity Level: More active Babies, such as when they crawl or play, may pant more since they are using more energy.
5. Environmental Stimuli: Babies may pant as a result of being excited by novel and exciting sights, noises, and surroundings.
Does a Baby Pant Normally?
To ascertain whether a baby’s panting is typical, it is necessary to comprehend many factors:
1. Contextual Normalcy: It’s common to pant when playing or feeling ecstatic. It indicates how much your child is interacting with the outside world.
2. Frequency and Duration: Generally, there’s no need to worry if you sometimes pant but it stops soon the adrenaline wears off.
3. Accompanying Symptoms: Keep an eye out for additional symptoms that can point to an issue, such as bluish skin, a persistent cough, or hard breathing.
4. Developmental Consistency: Your baby’s panting is probably a typical aspect of their growth if it corresponds with their developmental stage and happens in predictable situations.

Monitoring and Managing Baby Panting
Controlling a baby’s panting requires attentive attention and action:
• Observation: Pay special attention to the timing and frequency of your baby pants. Keep track of any trends or triggers.
• Calming Techniques: If your baby’s panting appears to be upsetting, try calming them down with some quiet time, gently rocking, or gentle singing.
• Environmental Control: Take charge of your baby’s surroundings’ stimulus. Refrain from overstimulating and provide a tranquil environment.
• Consultation: See your doctor for advice if you’re worried about the type or frequency of the panting.
Pediatric Advice on Baby Panting
Pediatricians frequently offer insightful commentary about a baby’s panting:
• Normal Developmental Behavior: The majority of physicians concur that a baby’s occasional panting is a typical developmental stage.
• Signs to Watch for: Parents are advised to keep an eye out for any indications of respiratory distress or other medical problems.
• Regular Check-ups: It’s important to schedule routine pediatric appointments to evaluate your baby’s general health and address any issues.
• Parental Intuition: Have faith in your gut. It’s advisable to get expert help if something seems strange about your baby’s breathing.

Preventing Triggers of Rapid Breathing
To stop things from making a baby breathe too quickly:
• Gradual Exposure: To prevent overstimulating your infant, introduce new situations and settings little by little.
• Routine and Predictability: Provide your infant with a routine that gives them a sense of security and predictability.
•Observation of Triggers: Recognize and comprehend what triggers your baby’s excitement or overstimulation, and adjust your behavior accordingly.
• Balanced Stimulation: Throughout the day, offer a mix of relaxing and stimulating activities.
My Experience
In my experience, it was first both fascinating and disturbing to see my infant pant. I saw that it frequently occurred while we were playing or when we were introducing new toys. It was a display of their growing curiosity and enthusiasm, about the world. However, I also realized the importance of being vigilant for any patterns or signs of uneasiness, in their behavior. Speaking with our physician gave me comfort and clarity on this normal stage of my child’s growth. It’s an instructive and observational journey filled with moments of delight and discovery.

Conclusion
In conclusion, a typical and usually natural occurrence is a baby panting while they are aroused. It’s a sign of your baby’s growth—both, in terms of their emotional development—. Demonstrates their curiosity and enthusiasm, for the world. However to ensure the safety and welfare of our children parents need to stay informed, observant, and open-minded. Important elements in this path include recognizing when to seek medical counsel, comprehending the reasons and patterns of panting and getting regular pediatric checkups. Knowing that you’re giving your child the finest care and attention possible for their growth and happiness, enjoy these times of their development with delight and assurance.
FAQs
1. Is it typical for my infant to pant in anticipation?
Yes, panting is a natural reaction of excitement in newborns. It shows how their respiratory system and emotional reactions are developing.
2. When is my baby’s panting cause for concern?
Seek medical attention from a pediatrician if coughing, bluish skin, or prolonged panting are present.
3. Is there anything I can do to stop my baby’s breathing?
Your baby’s breathing can be regulated with the use of gentle calming techniques such as rocking, soft singing, or creating a peaceful environment.
4. Is there a distinction between a baby’s panting and breathing difficulties?
Breathing problems can be persistent and accompanied by other distress signals, although panting is usually transient and associated with excitement.
5. Are there any activities I can do to assist in managing my baby’s breathing?
Although there is no need for specialized workouts for panting, maintaining a regular physical activity schedule and stimulating surroundings can improve respiratory health in general.
6. How can I tell the difference between ordinary panting and a more serious condition?
Normal panting normally lasts a short while and happens in certain contexts, such as during recreation. It can be more dangerous if the panting is ongoing, seems to be exerted, or is accompanied by additional symptoms.
7. Should I keep an eye on my infant’s breathing while they sleep?
It’s a good idea to watch how your infant breathes when they sleep. Talk to your pediatrician if you observe any abnormalities or persistent panting.